
- Organ Name: Hand, (Hands plural)
- Organ Purpose: Allow manipulation of objects
- Organ Location: At the end of each arm
- Organ Count: 2, left hand and right hand
- Organ FMA ID: 9712
- Organ TA ID: A01.1.00.025
28 Hand Facts for Kids
- A hand is a five finger appendage located at the end of a human forearm.
- Hands allow humans to manipulate objects, lift heavy objects and complete small complex tasks with their fingers.
- A human with no biological abnormalities has two hands, a left hand and a right hand.
- A human with no biological abnormalities has five fingers on each hand.
- The five fingers on the human hand are the thumb, index finger, middle finger, ring finger and little finger.
- Some anatomists don’t consider the thumb a finger, and in those situations the hand is considered to have four fingers and a thumb.
- A person can be right-handed or left-handed.
- A person who is right-handed person will use their right hand most of the time to complete tasks, while a left-handed person will use their left hand.
- It’s estimated that 90% of the human population is right-handed.
- The human hand is divided into three main sections.
- The three main sections of the human hand are the carpus, metacarpus and fingers.
- The human hand is made up of 27 different bones.
- The human hand has 8 carpal bones.
- The human hand has 5 metacarpal bones.
- The human hand has 14 phalange bones.
- The phalange bones are also known as finger bones.
- The bones in the human hand make up about 25% of all the bones in the human body.
- The human hand has over 30 muscles that work together with joints, bones and nerves to give mobility.
- The hands receive their blood supply from two main arteries.
- There are skin and muscle on the human hand are powered by three nerves.
- The three nerves powering the human hand are the radial nerve (nervus radialis), the median nerve (nervus medianus) and the ulnar nerve (nervus ulnaris).
- The palm of the human hand has over 17,000 touch receptors and free nerve endings.
- Over the course of an entire human lifespan the fingers on a human hand bend and stretch over 25 million times.
- Humans have the most advanced hands and fingers on the planet, but other animals also have forearm appendages that are anatomically classified as hands.
- Animals that have appendages that are anatomically classified as hands are chimpanzees, lemurs and monkeys.
- The Foundational Model of Anatomy Ontology (FMA) ID for a human hand is 9712.
- The Terminologia Anatomica (TA) ID for a human hand is A01.1.00.025.
- The Medical Subject Headings (MeSH) ID for a human hand is D006225.
Pictures of Hands

A picture of a human left hand.Credit: Ghetty Images

A picture of a human right hand.Credit: Ghetty Images
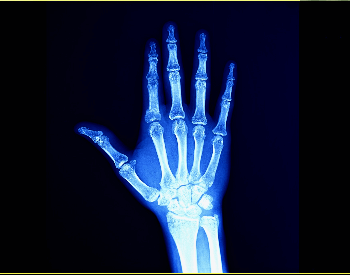
A picture of an x-ray of a hand.Credit: Ghetty Images
Additional Resources on the Human Hand
- How the Hand Works Works – Discover how the hands work and what they do on the NIH website.
- Hand Anatomy – Britannica – Learn more about your hands on the Britannica website.
- Hand – Wikipedia – Explore the Wikipedia website to learn more about your hands.
