- Organ Name: Brain
- Organ Location: Within the skull bones of the head
- Organ System: Central Nervous and Neuroimmune systems
- Organ Purpose: Controls all body processes
- Organ Weight: Between 2.6 and 3.1 pounds
- Organ Length: 6.5 inches (average)
23 Brain Facts for Kids
- The human brain is the main component of the human nervous system.
- The human brain is mostly made of blood vessels, glial cells, nerve cells (neurons), neural stem cells (NSCs).
- The human brain controls almost all the functions of the human body, including thoughts, memories and emotions.
- The human brain is in and protected by the human skull (cranium), suspended in a fluid called cerebrospinal fluid.
- The human brain uses around 20% of the energy produced by your body.
- The human brain continues to grow from birth up to the age of 18.
- The average weight of an adult human brain is between 2.6 and 3.1 pounds or about 2% of total body weight.
- It’s estimated that the human brain has 86 billion neuron cells and 85 billion non-neuron cells.
- The human brain has two different cerebral hemispheres.
- The two cerebral hemispheres of the human brain are the right hemisphere and left hemisphere.
- The right and left hemispheres of the human brain are redundant and there are many brain functions that can happen in both hemispheres.
- The left hemisphere of the human brain controls the right side of your body and is connected to the nerves on the left side of both your eyes.
- The right hemisphere of the human brain controls the left side of your body and is connected to the nerves on the right side of both your eyes.
- The human brain has four lobes, and they are the frontal lobe, parietal lobe, occipital lobe and the temporal lobe.
- The frontal lobe is responsible for some very important cognitive skills, like judgement, problem-solving and emotions.
- The parietal lobe is responsible for sensory information, like interpreting words and sounds.
- The occipital lobe is responsible for interpreting input from the retina and understanding color, movement and light.
- The temporal lobe is responsible for things like memory, organization and hearing.
- The human brain is quite large (over three times as large) compared to other mammals of similar size.
- In 2007, the World Health Organization estimated that 6.8 million people die annually due to neurological disorders.
- An example of some neurological disorders is Alzheimer disease, brain tumors, CTE, dementias, head trauma, multiple scleroses, Parkinson’s disease and a stroke.
- Chronic Traumatic Encephalopathy (CTE) is a brain disease common in people with repetitive brain trauma, like athletes and military veterans.
- The human brain is very complex and scientists are still learning about this mysterious and powerful organ.
Pictures of the Human Brain
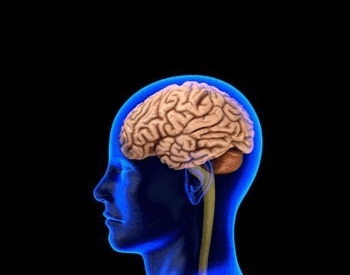
An illustration of the brain inside the human head.Credit: NSF
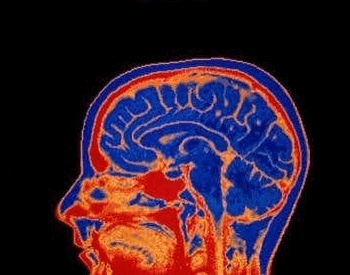
An MRI (Magnetic Resonance Image) of the human brain.Credit: Mehau Kulyk / SPL
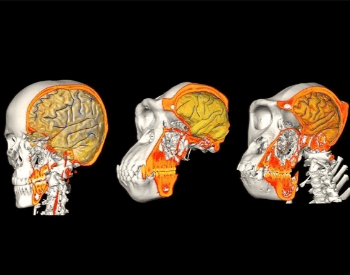
A image comparing the brain size of humans to primates.Credit: J.L. Alatorre Warren / UZH
Additional Resources on the Human Brain
- The Basics of the Human Brain – Read about the basics of the human brain on the National Institutes of Health.
- The Human Brain Anatomy and Function – Visit the Visible Body website to learn about the anatomy of the brain.
- The Structure and Function of the Brain – Discover the function and structure of the human brain on the Northeastern University website.
- Human Brain – Wikipdia – Find more cool facts about the human brain on the Wikipedia website.
