- Name: Cell (biological unit)
- Location: Throughout the human body
- System: All human systems have some sort of cells
- Purpose: Wide range of functions, including oxygen transportation and protection
- Types of Cells: Around 200 different cells in the human body
- FMA ID: 68646
23 Cell Facts for Kids
- Cells are the smallest biological unit of life found in all organisms.
- Cells are sometimes referred to as the “building blocks of life”.
- Between 1632 and 1723 the first protozoans and bacteria were observed by Antonie van Leeuwenhoek.
- In 1665, Robert Hooke first observed cells by looking at cork under an early compound microscope.
- The word “cell” was coined by Robert Hooke in 1665, in a book he published call Micrographia.
- Cell theory was a theory suggested in 1839 that all living organisms were made up of cells.
- The cell theory was developed by Theodor Schwann and Matthias Jakob Schleiden.
- Organisms can have one of two classifications, unicellular or multicellular.
- A unicellular organism only has one cell. An example of a unicellular organism is bacteria.
- A multicellular organism has more than one cell. An example of a multicellular organism is a human.
- There are two different types of cells, eukaryotic or prokaryotic.
- Eukaryotic cells have a nucleus can be a unicellular or multicellular organism.
- Prokaryotic cells do not have a nucleus and are unicellular organisms.
- Cell division is the process where one cell divides itself into two or more cells.
- The division of cells was first observed in 1835 by Hugo von Mohl.
- It’s estimated cells first appeared on Earth around 3.5 billion years ago.
- It’s estimated the average human body has about 40 trillion cells.
- It’s estimated the human brain alone contains 80 billion cells.
- The human body has around 200 different types of cells, like blood cells, bone cells, fat cells, skin cells and stem cells.
- Blood cells in the human body include red blood cells, white blood cells and platelets.
- Bone cells in the human body include osteoblasts, osteoclasts, osteocytes, and osteoprogenitor cells.
- The branch of biology that deals with the study of cells is called cell biology.
- A person who studies cell biology is known as a cell biologist or a cellular biologist.
Human Cell Pictures
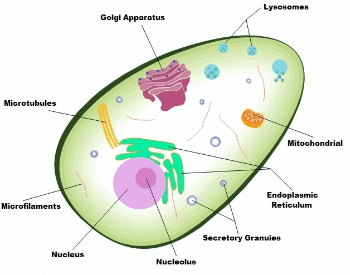
A diagram showing thecomponents and structure of a human cell.Credit: PSlides
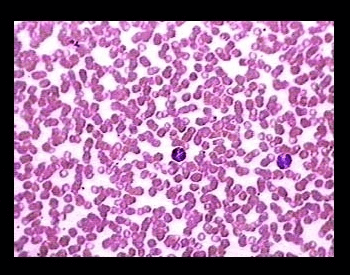
A picture of human blood cells under a microscope (400x).Credit: Austin Community College
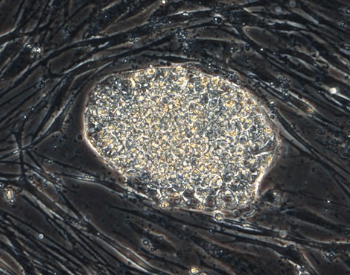
A picture of human embryonic stem cells under a microscope (200x).Credit: Jack Mosher, PhD
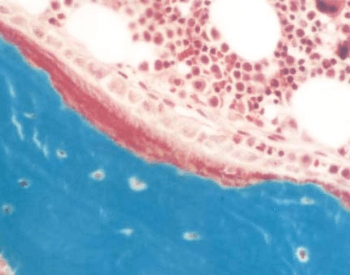
A picture of human bone cells under a microscope.Credit: Russ Turner
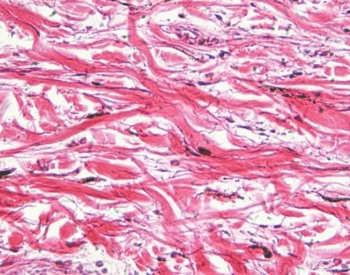
A picture of human skin cells under a microscope.Credit: University of California
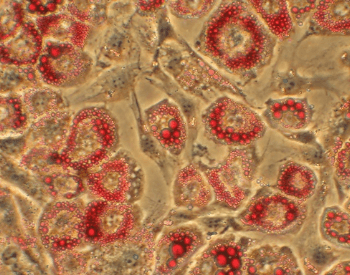
A picture of human fat cells under a microscope.Credit: University of California
Additional Resources on Human Cells
- What is a Cell? – Learn what a cell is and what they do on the U.S. National Librarty of Medicine website.
- Cell Structure and Components – Discover the structure and components of cells on the National Cancer Institute website.
- Cell (Biology) – Britannica – Read more interesting facts about cells on the Britannica website.
- Cell (Biology) – Wikipedia – Find more cell facts on the Wikipedia website.
