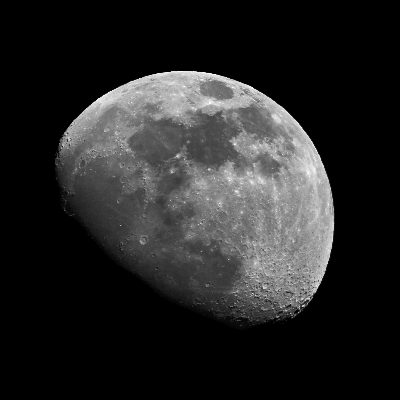

- Moon Name: Luna or The Moon
- Formed: 4.51 billion years ago
- Discovered: Over 5000 years ago
- Distance from Earth: Between 225,633 miles (perigee) and 252,088 miles (apogee)
- Distance from the Sun: 93,205,678 miles on average
- Time to Orbit Around Earth: About 27 Days
- Total Surface Area: 23,549,968 square miles
98 Moon Facts for Kids
- The Moon formed shortly after the planet Earth, about 4.51 billion years ago.
- The gap between Earth and Moon’s formation is estimated to be between 30 and 50 million years.
- The Moon is Earth’s only natural satellite (a moon). A natural satellite is a space object that orbits around a planet on a fixed axis.
- The Moon is about a quarter (1/4th) of the Earth’s size.
- The Moon is the closest natural satellite (a moon) to the Sun.
- The Moon is the fifth largest moon in our Solar System.
- The Moon is the second densest moon in our Solar System.
- The radius of Earth’s only Moon is about 1,079 miles.
- The closest the Moon gets to Earth is 225,633 miles (perigee).
- The farthest the Moon gets from Earth is 252,088 miles (apogee).
How is the Moon Related to the Sun?
- It will take about thirty earth-like planets to cover the distance between the Earth and the Moon.
- It takes the Moon about 27.3 days to orbit the planet Earth. The exact duration is 27 days, 7 hours, 43 minutes, and 11.6 seconds.
- A Lunar Month lasts 29.53 days (29 days, 12 hours, and 44 minutes), measuring from one New Moon to the next.
- The Moon is the second most visible celestial object in our sky, next to our Sun.
- The Moon is 400 times smaller than the sun.
- The Moon is similar to the Sun as it rises in the east and sets in the west. However, it moves from the north end to the sound end and back continuously during its phases.
- The Moon appears the same size as the Sun when we look at the sky. This is because the Moon is much closer to the earth than the Sun.
- A lunar eclipse is when the Moon passes behind the Earth and enters it shadow. This eclipse occurs after sunset (between twilight and dawn).
- A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon blocks the sunlight by coming between the sun and the earth. This eclipse occurs in the daytime (between dawn to dusk).
- The Moon is very slowly leaving Earth’s orbit. It moves about 1.5 inches farther away from Earth every year. The total lunar eclipse will not be possible after 600 million years. The Moon will be too far off from the Earth by then.
- Even scientists are not fully sure about how the Moon was formed. According to popular theory, a huge rock named Theia (the size of Mars) crashed into our earth. This collision created several broken parts which came together to form the Moon.
What Can We Find on the Moon?
- The Moon has no atmosphere but is dusty and has a rough surface.
- The Moon has large and wide craters, mountains, and planes made of lava. These craters are said to be made by various asteroid collisions.
- The rocky parts of the Moon are said to have large deposits of iron, magnesium, sulfur, etc.
- The dark areas on the Full Moon are the seas. These have Latin names like Mare Serenitatis (Sea of Serenity) and Mare Frigoris (Sea of Cold). These seas are nothing but lava.
- The tallest mountain on the Moon is called Mons Huygens. It is 4700 meters high (approximately half of Mt. Everest in the Himalayas).
- The largest crater on the Moon is called Bailly. It covers a surface area of 26 square miles.
- The Moon is the only object in our Solar System to have been physically visited by a human.
- The Moon’s surface area is the size of the African continent.
- On the Moon, you only weigh about 16.5% of what you weigh on Earth. This is due to how much weaker the gravity on the Moon is compared to Earth.
- The Moon’s gravitational influence on Earth is what causes body tides, ocean tides and lengthening of days.
- The gravitation pull is at its maximum on New Moon and Full Moon nights. This causes the tides to rise high. The high tides are called Spring Tides.
- The lowest tides occur when the Moon is a quarter of its size. These tides are called Neap Tides.
- The Moon cannot produce its own light. It shines in the night sky by reflecting sunlight.
- The Moon has extreme temperatures, ranging from -153°C to 127°C. This depends on the extent of sunlight falling on the Moon’s surface.
- It’s estimated that the Moon did not have any volcanic flows in the last three billion years.
Facts about Moon Phases
- The Moon as eight phases: New Moon, Waxing Crescent, First Quarter, Waxing Gibbous, Full Moon, Waning Gibbous, Last Quarter and Waning Crescent.
- New Moon is when there is no Moon in the night sky.
- A Full Moon is when we see the round Moon shining bright in the dark sky.
- Waning is when the Moon gradually decreases in size (this happens during the period from Full Moon to New Moon).
- Waxing is the opposite of waning, where the Moon grows in size (from New Moon to Full Moon).
- The Moon doesn’t really change its size every day. This illusion is created by its changing position and the angle of sunlight.
- The Moon’s phases are due to its movement in space. We can see only the part of the Moon illuminated by sunlight. The rest remains dark and is not visible to the naked eye.
- You can always see the Full Moon if you travel to the sun and stand on it. Don’t try it, though. 😉
- The Moon also rotates on its own axis while revolving around the earth. We can only see 60% of the Moon, at the most.
- The side of the Moon visible from the earth is called the near side. The part we cannot see is called the far side.
- We see a slight crescent Moon in the twilight sky a couple of days after the New Moon. This crescent is illuminated by earthshine. Earthshine is the sunlight reflected from the earth’s surface. This falls on the Moon and highlights its presence.
- You can see only the Full Moon directly overhead at midnight. The Moon has different rising and setting times in each phase.
- You can see the Moon even during the daytime. Look in the opposite direction of the sun. This doesn’t happen every day.
- Sometimes, the month of February can pass without a single Full Moon. The months with 31 days might even have two Full Moons or New Moons on rare occasions.
- The second Full Moon in the same month is called a Blue Moon. It tends to happen every three years.
- You can sometimes see a ring around the Moon. This is called Lunar Ring and is caused by the ice crystals in the cirrus clouds in the night sky. They reflect light at an angle of 22 degrees, thus creating a halo/ ring-like appearance around the moon.
- In countries like India, the Lunar Ring is used by people to predict rains. A smaller ring suggests rains at a later date, while a large ring implies rains in the next few days.
Moon and Space Research
- The decade from 1950 to 1960 had the highest activity of explorations on the Moon. The fascination with exploring the Moon’s surface continues even today.
- The Soviet Union Luna 2 spacecraft was the first spacecraft to reach the surface of the Moon in 1959.
- The Soviet Union Luna 3 spacecraft was the first spacecraft to take pictures of the far side of the Moon.
- The Soviet Union Luna 9 spacecraft was the first spacecraft to successfully land on the Moon.
- The Soviet Union Luna 10 spacecraft was the first spacecraft to successfully orbit the Moon unmanned.
- In 1964, the Ranger 7 spacecraft by NASA (National Aeronautics and Space Administration) took 4000 pictures of the Moon in fifteen minutes.
- The United States of America’s Apollo 8 mission was the first successful manned orbit of the Moon.
- The United States of America’s Apollo 11 mission was the first successful manned mission where a human walked on the Moon in 1969.
- Neil Armstrong was the first person to land on the Moon in 1969, along with Buzz Aldrin. The lunar ship was named Eagle. However, there’s a controversy surrounding the pictures/ videos as many people noticed the American flag fluttering in the background (which is impossible since the Moon has no atmosphere).
- All Apollo missions brought about 850 pounds of rocks from the Moon.
- It is estimated that the footprints left by Apollo astronauts on the Moon will last for a minimum of ten million years.
- In the 1950s, the United States had a secret project called Project A119. The plan was to detonate a nuclear weapon on the surface of the Moon as a show of strength during the Cold War.
- Commander Alan Shepard, an American astronaut, traveled about 9000 feet on the Moon’s surface in 1971. He was the oldest person to walk on the Moon (at 47 years).
- In 1990, Japan launched its first spacecraft into the Moon’s orbit. It was the third country to do so.
- China is the third country after Russia and the US to touch the near side of the Moon. This event happened in 2013.
- China sent its first spacecraft, Chang`e-4, to the far side of the Moon in 2019.
- There are six American flags on the Moon (planted by different astronauts).
- Out of the twelve people who have walked on the moon, all of them are Americans.
- In 1967, an International law was established to prevent nations from staking a claim on space objects. Neither the Moon nor other planets and natural objects can be owned by any nation.
- The continuous research studies by different countries conclude that the Moon does have water in small quantities. The first discovery of water on the Moon was in 2009.
- ISRO’s (Indian Space Research Organization) Chandrayaan-1 confirmed that there was lunar water, and it was present in ice/ frozen form in the shadowed craters located at the poles.
Moon and Myths from Around the World
- The Moon has been a part of various folklores from different countries and civilizations. Each culture has its own theory, beliefs, and myths about the Moon.
- The Romans call the Moon Luna.
- The Ancient Greeks referred to the Moon as Cynthia, Selene, and Hectate.
- The Maori from New Zealand believes that a woman lives on the Moon. They call her moon Rona.
- The myth about a lady on the Moon is common in many other cultures.
- The Maori people also believe that the Moon is a man and has a wife and two daughters. They believe that the moon’s phases have an effect on women’s reproductive cycle.
- The indigenous people from Africa consider the Moon a male God, Mawu. The sun is a female God (goddess), Liza. According to their lore, the eclipse occurs when Mawu and Liza meet in the sky.
- In the Mayan civilization, Ixchel is considered one of the many Moon Goddesses. She is the Grandmother of the Moon and represents fertility and childbirth. She is also the Goddess of Weavers.
- According to the Aztec culture, the Moon God is called Tecciztecatl. He shares a few similarities with the Moon Gods from Asian cultures.
- The Moon God in Hinduism is called Chandra and Soma. As Soma, he rules over fertility and medication.
- The Moon is a female in most cultures, though it is a male in some indigenous cultures like Hinduism, etc.
- The Japanese, Chinese, Indian, and a few other countries talk about a rabbit on the Moon. The significance and story of the Moon and rabbit change from one culture to another.
- A few Native American tribes take the moon hostage, while a pair of antelopes have the responsibility of saving it. The story goes that a coyote gets the moon first and tosses it into the river.
Few Interesting Tidbits about the Moon
- The first map of the Moon was created by Galileo in 1609. He did it by inventing a device that could magnify objects up to 20 times (like a telescope).
- Anaxagoras, an ancient Greek philosopher of nature and cosmology, discovered the actual cause of eclipses. He was exiled to Lampsacus for saying that the Moon was a rock and not a goddess.
- Franz von Paula Gruithuisen claimed to have seen the Lunarians in the 1820s when he was observing the moon from his telescope. Lunarians are supposedly the beings/ creatures on the Moon.
- The Full Moon of each month is associated with a specific event from the season by the Algonquin Native American tribes. They use terms like Beaver Moon, Wolf Moon, Snow Moon, and Worm Moon.
- The Full Moon in each month has a different name, depending on the region. The names were given by the indigenous people who were mostly into agriculture.
- January: Old Moon, Moon After Yule, Wolf Moon
- February: Hunger Moon, Snow Moon
- March: Worm Moon, Sap Moon, Lenten Moon, Crow Moon
- April: Frog Moon, Egg Moon, Grass Moon
- May: Milk Moon, Planting Moon
- June: Strawberry Moon, Rose Moon, Flower Moon
- July: Hay Moon, Thunder Moon
- August: Green Corn Moon, Grain Moon
- September: Harvest Moon, Fruit Moon, Barley Moon
- October: Hunter’s Moon, Harvest Moon (the month depends on Equinox)
- November: Frosty Moon, Beaver Moon, Hunter’s Moon (the next one after Harvest Moon)
- December – Long Night Moon (as it occurs before winter solstice), Moon Before Yule
Other Plants and Their Moons
- Other planets have a varying number of moons.
- Mars has two moons, Deimos and Phobos. Both moons were discovered in 1877 by Asaph Hall.
- Mercury and Venus don’t have any moons (natural satellites) orbiting around them.
- Saturn has the maximum number of moons. Eighty-two were discovered until now, and seventeen of these moons orbit in a reverse (backward) direction.
- Neptune’s moons have names from Greek mythology.
- Tritan is one of Neptune’s moons and is the same size as Pluto.
Pictures of the Earth’s Moon

A photo of a rare full moon.Credit: NASA

A photo of the near side of the Earth’s moon.Credit: NASA
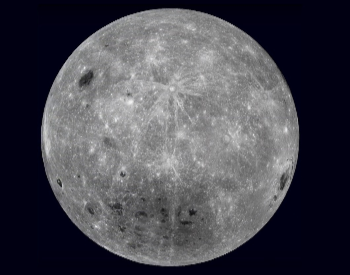
A photo of the far side of the Earth’s moon.Credit: NASA
Additional Resources on the Earth’s Moon
- Moon Facts: Fun Information About the Earth’s Moon – Learn more fun facts about the Earth’s moon on the Space.com website.
- In Depth | About the Moon – Moon: NASA Science – Find more in depth information about the Earth’s moon on the NASA website.
- Google Moon – Tour the surface of the Earth’s moon using Google’s moon maps.
- Moon – Wikipedia – Discover more interesting facts about the Earth’s moon on the Wikipedia website.
