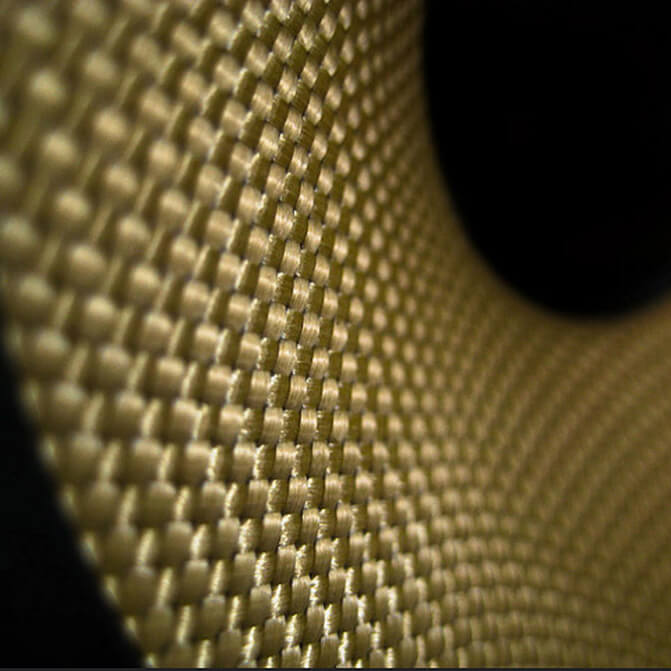
Developed by Stephanie Kwolek at DuPont in 1965, Kevlar is a strong heat-resistant and high-strength synthetic fiber. Initially, kevlar is spun into ropes or fabric sheets you can either use as such. If not, you can also use it as an ingredient in the composite material components.
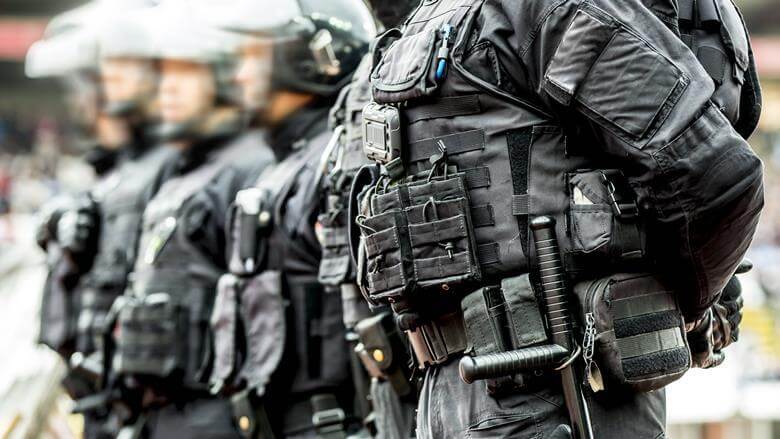
Though it’s a synthetic fiber, its usage is very different from the other synthetic fibers. For example, kevlar is mostly used in manufacturing bicycle tires, racing sails, bulletproof vests, among others.
If these facts about this wonder synthetic fiber seem interesting to you, the below kevlar facts will shake your mind. So, let’s dive right into this.
- Common name: Kevlar
- IUPAC name: Poly(azanediyl-1,4-phenyleneazanediylterephthaloyl)
- Inventor: Stephanie Kwolek, an American chemist
- CAS number: 24938-64-5
- Chemical formula: [-CO-C6H4-CO-NH-C6H4-NH-]n
60 Kevlar Facts for kids
- Kevlar or Poly-paraphenylene terephthalamide (K29) was invented by an American chemist Stephanie Kwolek while working for DuPont.
- Kevlar was first used in the 1970s as an alternative for heavy steel in racing tires. This was also the main motivation for Stephanie Kwolek to come up with kevlar.
- Kevlar has a high tensile strength-to-weight ratio. Due to this, it’s excessively used in bicycle tires, bulletproof vests, and racing sails.
- It’s five times stronger than regular steel.
- Kevlar is also popular in the manufacturing of marching drumheads.
- Kevlar is also utilized for mooring lines and other underwater uses.
- Kevlar shares its chemical structure with another fiber called Twaron, developed by Akzo.
- The production of kevlar is very expensive.
- There are several grades of kevlar available in the market with unique features and for different applications. For example, Kevlar K29, K49, K100, K119, K129, K149, AP, XP, KM2, etc.
- Upon spinning into a roll, the resulting kevlar fiber roll has a tensile strength of 3,620 MPa and 1.44 relative density.
- The high strength of kevlar is due to its inter-chain bonds.
- Some additional strength is provided to the kevlar by the aromatic stacking interactions between adjacent strands.
- The fiber’s structure contains rigid molecules which manage to form planar sheet-like structures instead of the silk protein.
- The strength and resilience of kevlar fabric stay the same down to even the cryogenic temperatures (−196 °C).
- Kevlar is slightly stronger at lower temperatures than at higher temperatures.
- Kevlar’s strength decreases by almost 10–20% at higher temperatures.
- It is highly used in cryogenics owing to its low thermal conductivity and high strength.
- It’s highly used in the manufacturing of safety equipment such as combat helmets, ballistic face masks, and ballistic vests.
- Kevlar is also a hot choice for manufacturing gloves, sleeves, jackets, etc.
- Articles of clothing designed to protect users from cuts, abrasions, and heat are also produced from kevlar.
- Kevlar-based gears are lighter, thinner, and durable than other materials used earlier.
- In simple words, kevlar is a form of super-strong plastic.
- Kevlar first came in only two varieties – Kevlar 29 and Kevlar 49. All other forms were a result of several applications.
- Kevlar is not cotton.
- Kevlar is an example of a chemical called synthetic aromatic polyamides or aramids.
- Due to its high tensile strength, kevlar decomposes only at about 450°C (850°F).
- It can withstand high temperatures without melting.
- Nomax is the sister material of kevlar.
- Kevlar can be ignited.
- Kevlar slightly decomposes after long exposure to UV rays.
- Kevlar can resist attacks from many different chemicals.
- Kevlar has very poor compressive strength. You can easily squash or squeeze it with bare hands. This is the reason why kevlar is not used as a replacement for steel in buildings or construction where high compressive strength is necessary.
- Kevlar’s production involves two stages. In the first stage, you have to produce the basic plastic and then turn it into fibers.
- You can use kevlar as such or as a composite material.
- Kevlar is an excellent anti-ballistic material.
- Kevlar is around 5.5 times less dense than steel. The density of kevlar is 1.44 grams per cubic centimeter, and that of steel is 7.8-8 grams per cubic centimeter.
- Kevlar weighs less than steel.
- The molecules of kevlar are organized in regular parallel lines.
- The first-ever commercial use of kevlar was in a racing car as a replacement for steel.
- It is very easy to clean.
- Kevlar is also used in brake pads.
- It is over ten times stronger than steel in tensile strength.
- Kevlar is highly flexible.
- It is manufactured by a chemical company called DuPont.
- The high tensile strength of kevlar is due to the cross-linking of the chains with hydrogen bonds.
- Kevlar KM2 is used for enhanced ballistic resistance for armor applications.
- Kevlar is also used as the key material for paraglider suspension lines.
- Tennis racquets are also manufactured using Kevlar.
- Kevlar K149 was invented by Dr. Jacob Lahijani of DuPont in the 1980s.
- Kevlar AP has 15% higher tensile strength than K-29.
- Kevlar K100 is the coloured version of Kevlar.
- The PASGT helmet and vest used by US military personnel use Kevlar as the key component in the manufacturing process.
- Nike used kevlar for the first time in its shoes in 2013.
- Shoes like LeBron, HyperDunk, and Zoom Kobe VII use kevlar as the key component.
- Several tire manufacturing companies use kevlar in their tires to prevent them from deflating.
- Kevlar is used in fiber optic cables also.
- Kevlar is also heavily used as an acoustic core on bows for string instruments. This is due to its strength and flexibility.
- This synthetic fiber is also used in ropes and cables.
- Kevlar 149 is the best alternative in certain parts of aircraft construction. This is because it is less prone than carbon or glass fiber to break during bird collisions or poor & harsh weather.
- Several car companies use kevlar for backplates due to its high solidity and lack of interference with signal transmission.
Conclusion
At first impressions, kevlar might appear to you as an ordinary synthetic fiber. However, it is more than that. It’s the strongest synthetic fiber having several applications across numerous industries.
It has a unique production procedure, but the result is a high tensile strength material capable of withstanding high temperatures and pressures.