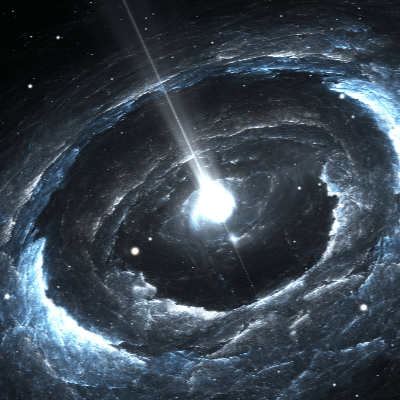

- Common Name: Neutron Star
- Type of Star: Giant Star (collapsed core)
- Mass: Between 1.1 and 2.1 mass
- First Discovered: 1967
- Discovered by: Jocelyn Bell Burnell
- Examples: PSR J0108-1431 and LGM-1
17 Neutron Star Facts for Kids
- A neutron star is a collapsed core of a giant star, created from a supernova explosion.
- The concept of a neutron star was proposed by Walter Baade and Fritz Zwicky in 1933.
- The first neutron star (pulsar) discovered was PSR B1919+21, by Jocelyn Bell Burnell on November 28th, 1967.
- Astronomers have discovered over 2,000 neutron stars and estimate there are over 100 million of them in our galaxy.
- Existing technology only allows us to detect neutron stars that are less than one million years old.
- The closet neutron star to our planet is RX J1856.5-3754. It’s around 400 light-years away.
- The average diameter of a neutron star is 6.2 miles.
- The average mass of a neutron star is 1.4 solar masses (one solar mass = the size of our sun).
- The average surface temperature of a neutron star is about 600,000 Kelvin.
- A neutron star has a very fast rotation, and a young neutron star can complete many rotations in just one second.
- A pulsar is a neutron star that rotates and emits pulses of radiation out of its poles.
- A magnetar is a neutron star that as massively powerful magnetic field. A magnetar can have a magnetic field that is a thousand trillion times greater than Earth’s.
- A radio-quiet neutron star doesn’t emit any detectable radio emissions, like a pulsar and doesn’t have the same magnetic field that as a magnetar.
- A neutron star can be part of a binary system. The binary systems discovered have included other multiple neutron stars, main-sequence stars, white dwarfs and red giants.
- Neutron stars are the smallest stars in our universe, however they are also the densest stars in our universe.
- To understand the density of a neutron star, imagine one the size of Manhattan Island. While it would only be 13 miles long, it would have a mass 1.5 times the size of our sun.
- A supernova explosion will create a neutron star, a block hole or destroy the progenitor.
Neutron Star Pictures

A photo of the Crab Puslar (PSR B0531+21), a young neutron star.Credit: NASA
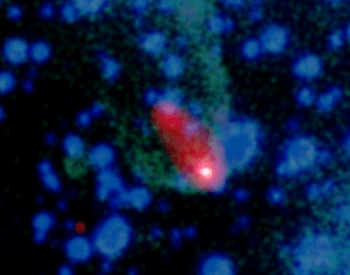
A photo of the Black Widow Puslar (B1957+20), a massive neutron star.Credit: NASA

A photo of PSR J0108-1431, the closest neutron star to planet Earth.Credit: NASA
Additional Resources with Neutron Star Facts
- Neutron Stars, Pulsars and Magnetars – Learn about these incredible types of stars on the NASA website.
- Neutron Stars – Study Astronomy Online – Discover more amazing facts about neutron stars on the Swinburne University website.
- Neutron Stars and their Gravitational Waves – Learn about the incomprehensible mass and density of neutron stars.
