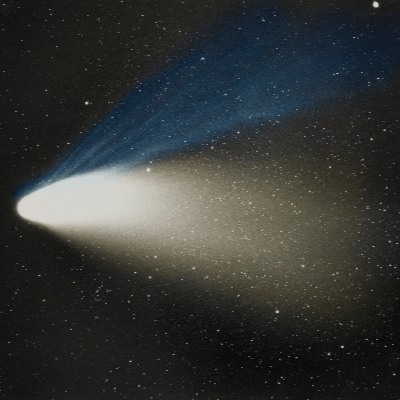

- Common Name: Comet Hale-Bopp
- Offical Designation: C/1995 O1
- Orbital Period: Between the years 2,520 and 2,533
- Last Close Earth Visit: April 1st, 1997
- Next Close Earth Visit: In the year 4385
- Discovered: July 23rd, 1995
- Discovered by: Alan Hale and Thomas Bopp
17 Comet Hale-Bopp Facts for Kids
- Hale-Bopp is a near-parabolic comet in our Solar System.
- Hale-Bopp is commonly called the Comet Hale-Bopp.
- Hale-Bopp is also known as The Great Comet of 1997 and C/1995 O1.
- The Hale-Bopp comet was discovered on July 23rd, 1995, by Alan Hale and Thomas Bopp.
- Alan and Thomas didn’t discover Hale-Bopp together. They both discovered it separately on July 23rd, 1995.
- The Hale-Bopp comet was so bright it could be viewed with the naked eye for 18 months.
- Astronomers estimated that the rotation period of the Hale-Bopp comet was just under 12 hours.
- Astronomers estimate that the current orbital period of the Comet Hale-Bopp is between 2520 and 2533 years.
- Astronomers estimated that Hale-Bopp’s nucleus was between 25 and 50 miles in diameter.
- Astronomers detected organic chemicals via spectroscopic observations of the Comet Hale-Bopp.
- The easy visibility and heavy media coverage of the Comet Hale-Bopp make it the most-observed comet in history.
- The Hale-Bopp comet was nearest to Earth (perihelion) on April 1st, 1997.
- Astronomers estimate that the last time Hale-Bopp was nearest to Earth was in 2215 BCE or 4,200 years ago.
- The next time the Comet Hale-Bopp will be nearest to Earth is around the year 4385.
- Astronomers think the Hale-Bopp comet may have almost collided with Jupiter in 2215 BC.
- The Hale-Bopp comet holds the record for the longest visibility by a naked eye. You could see it with your naked eye for 18 months, which is twice as longer as the previous record holder, the Great Comet of 1811.
- Members of a cult called the Heaven’s Gate thought a spaceship was flying behind the Hale-Bopp comet. Sadly, 39 members committed suicide, believing they would be teleported to that spaceship.
Comet Hale-Bopp Pictures
A picture of the Hale-Bopp Comet in 1999.Credit: NASA
A picture of the Hale-Bopp Comet in 1998.Credit: NASA

A picture of the Hale-Bopp Comet in 1997.Credit: NASA
Additional Resources with Comet Hale-Bopp Facts
- Hale-Bopp: The Bright and Tragic Comet – An excellent article by Space.com on the Hale-Bopp comet.
- View Images of the Hale-Bopp Comet – View over 5,000 photos of the Hale-Bopp comet, taken between 1995 and 2000 on the NASA JPL website.
- Comet Hale-Bopp – Wikipedia – Discover more awesome facts about the Hale-Bopp comet on the Wikipedia website.
