- Organ Name: Ear
- Organ System: Auditory system (sensory nervous system)
- Organ Purpose: Hearing and balance (equilibrioception)
- Organ Count: 2, left ear and right ear
- Organ FMA ID: 52780
- Organ TA ID: A01.1.00.005 and A15.3.00.001
27 Ear Facts for Kids
- The human ear is an organ that allows you to hear and keep your balance.
- The ear has two main functions, and they are hearing and balance.
- The ear transmits sound waves to the brain, allowing you to hear sounds.
- The ear allows you to hear by converting sound waves into nerve impulses that are sent to and interrupted by the brain.
- The ear allows you to feel the effects of gravity and acceleration, helping you keep your balance.
- There are three parts of the human ear, and they are the outer ear, middle ear and inner ear.
- The outer ear is the external visible part on the exterior of the human body.
- The middle ear is between both the outer ear and the inner ear.
- The inner ear is found in the bony labyrinth, which is a complex cavity in the temporal bone.
- Earwax (cerumen) is a waxy substance that the ear secretes for protection, cleaning and lubrication.
- The smallest bone in the human body is found in the ear, and it’s the stapes.
- Sounds that are higher than 85 dB (decibels) can damage your hearing.
- Hearing loss is defined as having partial to a complete inability to hear.
- Hearing loss is rated by degrees and there are seven degrees of hearing loss.
- The seven degrees of hearing loss are normal, slight, mild, moderate, moderately severe, severe and profound.
- A person with normal hearing loss can’t hear sounds less than -10 and 15 dB HL.
- A person with slight hearing loss can’t hear sounds less than 16 and 25 dB HL.
- A person with mild hearing loss can’t hear sounds less than 26 and 40 dB HL.
- A person with moderate hearing loss can’t hear sounds less than 41 and 55 dB HL.
- A person with moderately severe hearing loss can’t hear less than 56 and 70 dB HL.
- A person with severe hearing loss can’t hear sounds less than 71 and 90 dB HL.
- A person with profound hearing loss can’t hear sounds greater less than 91+ dB HL.
- Sign language is a process where one uses hand signs and motions to communicate with someone who can’t hear.
- A hearing aid is a small electronic device that can help improve the hearing of someone with hearing loss.
- The World Health Organization (WHO) estimates 466 million people worldwide have disabling hearing loss.
- The Foundational Model of Anatomy ID for the ears is 52780.
- The Terminologia Anatomica IDs for the ears are A01.1.00.005 and A15.3.00.001.
Pictures of the Human Ears
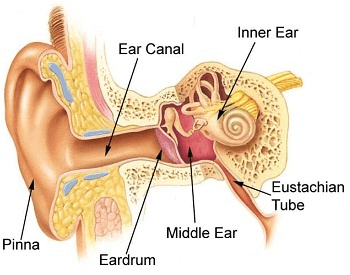
A diagram of the different parts of the human ear.Credit: Unknown
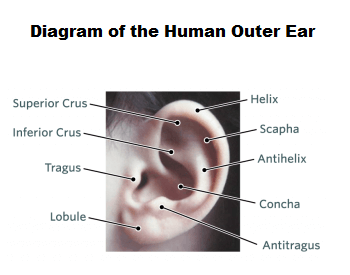
A diagram of the different parts of the outer ear.Credit: Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia
A picture of many different types of human earlobes.Credit: University of Delaware
Additional Resources on the Human Ears
- How the Ears Work – Basic information on the human ears work on the Johns Hopkins Medicine website.
- Ear Disorders – Learn about the different disorders that can affect the human ears on the MedlinePlus website.
- Human Ear – Britannica – Find more detailed information and facts about the ears on the Britannica website.
- Ear – Wikipedia – Find more ear facts and information on the Wikipedia website.
